Canadian home sales continued their upward trend in january as prices fell modestly
The Canadian Real Estate Association announced today that home sales over the last two months show signs of recovery. National sales were up 3.7% between December 2023 and January 2024, building on the 7.9% gain in December. The chart below shows that despite the two-month rise, sales remain 9% below their ten-year average. According to Shaun Cathcart, CREA’s Senior Economist, “Sales are up, market conditions have tightened quite a bit, and there has been anecdotal evidence of renewed competition among buyers; however, in areas where sales have shot up most over the last two months, prices are still trending lower. Taken together, these trends suggest a market that is starting to turn a corner but is still working through the weakness of the last two years.”
National gains were once again led by the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), Hamilton-Burlington, Montreal, Greater Vancouver and the Fraser Valley, Calgary, and most markets in Ontario’s Greater Golden Horseshoe and cottage country.
The actual (not seasonally adjusted) number of transactions was 22% above January 2023, the most significant year-over-year gain since May 2021. While that sounds like a resounding rise in activity, January 2023 posted the weakest transaction level in nearly twenty years.
There is pent-up demand for housing, and recent buyers are lured back into the market by the recent price decline and the fear that prices could rise significantly once the Bank of Canada starts cutting interest rates.
New Listings
The number of newly listed homes increased 1.5% month-over-month in January, although it remains close to the lowest level since last June.
“The market has been showing some early signs of life over the last couple of months, probably no surprise given how much pent-up demand is out there,” said Larry Cerqua, Chair of CREA.
With sales up by more than new listings in January, the national sales-to-new listings ratio tightened further to 58.8% compared to under 50% just three months earlier. The long-term average for the national sales-to-new listings ratio is 55%. A sales-to-new listings ratio between 45% and 65% is generally consistent with balanced housing market conditions, with readings above and below this range indicating sellers’ and buyers’ markets, respectively.
There were 3.7 months of inventory on a national basis at the end of January 2024, down from 3.8 months at the end of December and 4.1 months at the end of November. The long-term average is about five months of inventory.
Home Prices
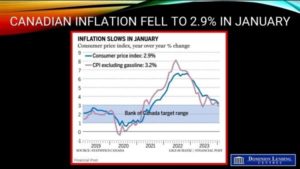
The Aggregate Composite MLS® Home Price Index (HPI) fell by 1.2% month-over-month in January 2024, adding to the 1.1% price decline in December.
Price descents of late have been predominantly in Ontario markets, particularly the Greater Golden Horseshoe and, to a lesser extent, British Columbia. Elsewhere in Canada, prices are mostly holding firm or, in some cases (Alberta and Newfoundland and Labrador), continuing to rise.
The Aggregate Composite MLS® HPI was up 0.4% year-over-year in January 2024, similar to readings over the past six months.
Bottom Line
Sales in December and January generally run at about half the peak spring season pace. That could be especially true this year, with interest rates likely to begin falling by mid-year. A strong housing rebound is coming. Housing markets have bottomed, buyer sentiment is improving and fixed mortgage rates have started declining.
Housing markets in Toronto, Vancouver and Montreal are relatively balanced again, and with the spring season, we will see a rise in new listings.
In other news, the inflation data released yesterday in the US were higher than expected, pushing rate-cut forecasts further out. With the strength in the US economy, the 5-year government of Canada bond yield has quietly risen more than 50 basis points this year.
Canada’s Housing Minister, Sean Fraser, said he expects the fall in interest rates this year to encourage builders to ramp up their activity, helping to alleviate some of the country’s crunched housing supply. At a news conference yesterday, the minister said, “My expectation is if we see a dip in interest rates over the course of this year, a lot of the developers that I’ve spoken to will start those projects that are marginal today.”
Sean Fraser, asked whether he’s concerned that Bank of Canada rate cuts will unleash pent-up demand and higher home prices, said lower borrowing costs should also lead to an increase in supply. Fraser said whatever happens with rates, the government’s course of action will remain the same. “We need to do everything we can as quickly as we can to build as many homes as we can. And that’s going to be true today and six months from now, regardless of what may happen in the interest rate environment that we’re dealing with.”
At a news conference last week, Bank of Canada Governor Tiff Macklem said that while he’s heard from developers who’ve indicated higher rates are delaying projects, lowering rates would have a more significant impact on demand.
“It’s very clear in the data that the effects of interest rates on demand are much bigger than those on supply,” he told reporters.