Lenders have started raising fixed mortgage rates again, with signs pointing to a short-term upward trend.

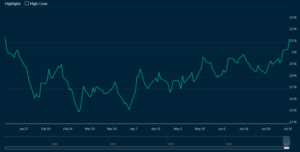
Fixed mortgage rates have been creeping upward over the past week, fuelled by a modest rebound in bond yields following stronger-than-expected economic data.
The increases were partly driven by rising U.S. Treasury yields, with the 5-year rising above 4% following stronger-than-expected inflation data. That, in turn, helped lift Canadian bond yields, which are closely linked to their U.S. counterparts.
On this side of the border, Canada’s strong June employment report added to the momentum. Since fixed mortgage rates are closely tied to government bond yields, the upward pressure was enough to prompt some lenders to raise pricing, particularly on 3- and 5-year terms.
Rate hikes of around five to 10 basis points (0.05 to 0.10 percentage points) were seen by some lenders over the past week, with further increases continuing into this week.
While the changes varied by lender, they reflect what some observers see as a short-term trend toward higher fixed rates.
“Some lenders responded by increasing their fixed mortgage rates on Friday and I expect others to follow,” wrote mortgage broker Dave Larock. “Those increases are consistent with my recent assessment that bond yields, and the fixed mortgage rates that are priced on them, now have an upward bias.”
Ron Butler of Butler Mortgage said the upward move in longer-term yields is also being shaped by broader fiscal pressures. “The spectre of growing government deficits all over the world is creating capacity concerns,” he told Canadian Mortgage Trends.
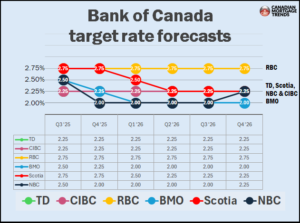
He added that 3- to 5-year fixed mortgage rates—currently in the 4% range—will likely stay around these levels for the next few months.
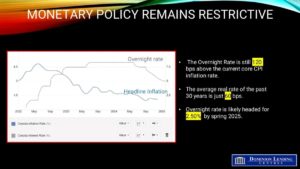
Inflation data firm expectations for BoC hold
Larock noted that while June’s jobs data may not significantly affect the Bank of Canada’s rate outlook, the June inflation results released Tuesday will. Statistics Canada reported that the country’s annual inflation rate ticked up to 1.9% in June, with core inflation measures remaining stubborn.
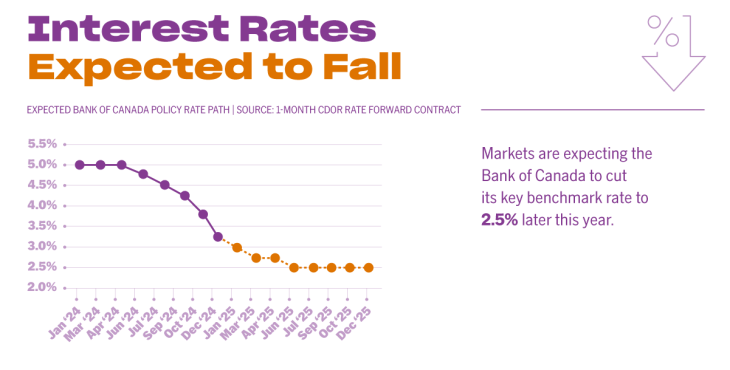
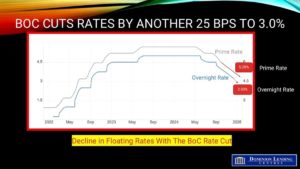
That firmed expectations the Bank of Canada will hold its key rate on July 30, which would mean no change for existing variable-rate and HELOC borrowers.
“The central bank will almost certainly hold this month,” Butler said, though he still sees the potential for a cut later in the year. “No cuts from the BoC in July or September seem likely, but I expect one in October or December as the economy worsens.”
Many fixed terms still closely priced
Despite the recent hikes, Larock pointed out that fixed rates remain below their long-term averages. Term premiums, which are typically the extra cost of locking in for longer, are starting to return, but many popular fixed terms are still priced similarly.
In cases where 3- and 5-year terms are comparable, Larock said he continues to favour the 5-year fixed.
He added that variable rates are likely to deliver the lowest overall borrowing cost over time, assuming rate cuts materialize as expected. But he cautions that variable-rate borrowers need to be prepared for continued volatility and higher payments if the timing of those cuts shifts further out.
“Anyone choosing a variable rate should do so only if they can live with its inherent potential for volatility and if they have the financial capacity to withstand higher costs (and, in some cases, higher payments) should my forecast prove incorrect,” he wrote.
This article was written for Canadian Mortgage Trends by: