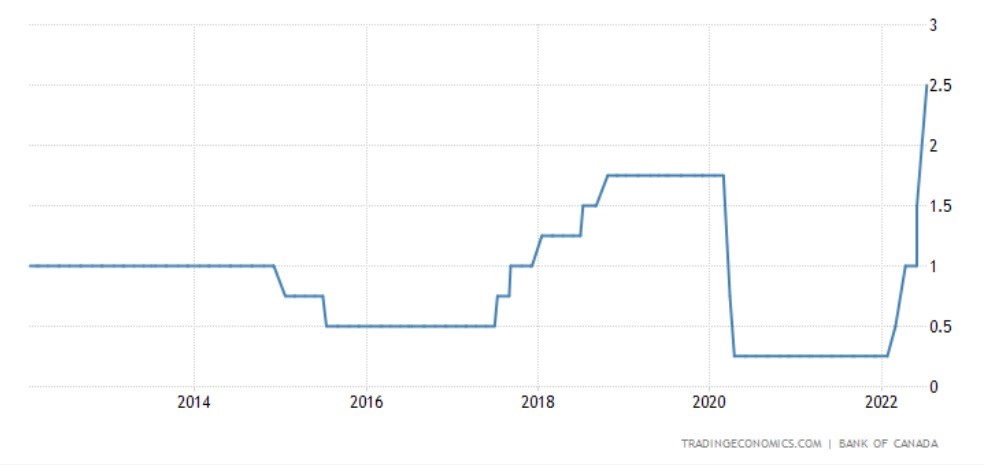
A Super-Sized Rate Hike, Signalling More To Come
The Governing Council of the Bank of Canada raised its target for the overnight policy rate by a full percentage point to 2-1/2%. The Bank is also continuing its policy of quantitative tightening (QT), reducing its holdings of Government of Canada bonds, which puts additional upward pressure on longer-term interest rates.
In its press release this morning, the Bank said that “inflation in Canada is higher and more persistent than the Bank expected in its April Monetary Policy Report (MPR), and will likely remain around 8% in the next few months… While global factors such as the war in Ukraine and ongoing supply disruptions have been the biggest drivers, domestic price pressures from excess demand are becoming more prominent. More than half of the components that make up the CPI are now rising by more than 5%.”
The Bank is particularly concerned that inflation pressures will become entrenched. Consumer and business surveys have recently suggested that inflation expectations are rising and are expected to be higher for longer. Wage inflation has accelerated to 5.2% in the June Labour Force Survey. The unemployment rate has fallen to a record-low 4.9%, with job vacancy rates hitting a record high in Ontario and Alberta.
Central banks worldwide are aggressively hiking interest rates, and growth is slowing. “In the United States, high inflation and rising interest rates contribute to a slowdown in domestic demand. China’s economy is being held back by waves of restrictive measures to contain COVID-19 outbreaks. Oil prices remain high and volatile. The Bank expects global economic growth to slow to about 3½% this year and 2% in 2023 before strengthening to 3% in 2024.”
Further excess demand is evident in the Canadian economy. “With strong demand, businesses are passing on higher input and labour costs by raising prices. Consumption is robust, led by a rebound in spending on hard-to-distance services. Business investment is solid, and exports are being boosted by elevated commodity prices. The Bank estimates that GDP grew by about 4% in the second quarter. Growth is expected to slow to about 2% in the third quarter as consumption growth moderates and housing market activity pulls back following unsustainable strength during the pandemic.”
In the July Monetary Policy Report, released today, the Bank published its forecasts for Canada’s economy to grow by 3.5% in 2022–in line with consensus expectations–1.75% in 2023 and 2.5% in 2024. Some economists are already forecasting weaker growth next year, in line with a moderate recession. The Bank has not gone that far yet.
According to the Bank of Canada, “economic activity will slow as global growth moderates, and tighter monetary policy works its way through the economy. This, combined with the resolution of supply disruptions, will bring demand and supply back into balance and alleviate inflationary pressures. Global energy prices are also projected to decline. The July outlook has inflation starting to come back down later this year, easing to about 3% by the end of next year and returning to the 2% target by the end of 2024.”
Bank of Canada Overnight Rate
Bottom Line
Today’s Bank of Canada reports confirmed that the Governing Council continues to judge that interest rates will need to rise further, and “the pace of increases will be guided by the Bank’s ongoing assessment of the economy and inflation.” Once again, the Bank asserted it is “resolute in its commitment to price stability and will continue to take action as required to achieve the 2% inflation target.”
At 2.5%, the policy rate is at the midpoint of its ‘neutral’ range. This is the level at which monetary policy is deemed to be neither expansionary nor restrictive. Governor Macklem said he expects the Bank to hike the target to 3% or slightly higher. Before today’s actions, markets had expected the yearend overnight rate at 3.5%.
Please Note: The source of this article is from SherryCooper.com/category/articles/